Here at i3 Simulations, we’re always up-to-date with new research in simulation, education, and Extended Reality (XR) technology. We’ve decided to share this knowledge through a monthly blog series, where we’ll be sharing the latest evidence on how XR simulations are transforming medical training.
Here’s what’s new this month: large-scale evaluations of Virtual Reality for medical education with literature and cohorts, and improving critical thinking skills in nursing education.
Toward the validation of VR-HMDs for medical education: a systematic literature review
Pedram, G. Kennedy, S. Sanzone – Virtual Reality (2023)
This literature review examines the use of VR headsets for training clinical skills to medical students and practitioners. It finds many ad hoc VR applications across medical contexts but with a lack of long-term validation and evidence of skill transfer to real clinical settings.
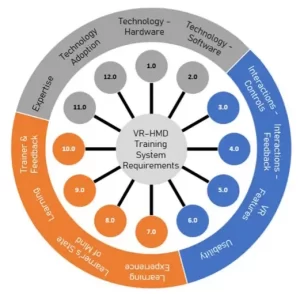
To address this gap, the authors distil 92 requirements into 11 categories to guide future VR training systems. The requirements cover aspects like controls, feedback, simulation features, learning experience, usability, required expertise, and adoption considerations. The goal is to enable more rigorous validation of VR as an effective medical education tool. Key gaps identified include a lack of studies on long-term skill retention and real-world transfer from VR training.
The proposed requirements framework aims to promote more systematic VR training designs and validation research to demonstrate real learning outcomes. This could strengthen the evidence base for VR as a viable medical education platform.
Mahling, R. Wunderlich, D. Steiner et al. – Journal of Medical Internet Research (2023)
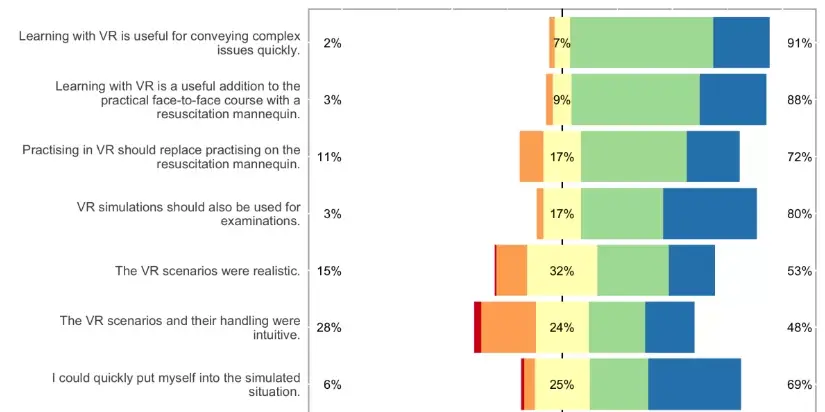
Researchers implemented a VR emergency medicine curriculum with 129 medical students. The VR scenarios enabled unlimited practice of challenging situations like cardiac arrest and trauma assessment. Overall, students responded extremely positively: over 90% felt VR quickly illustrated complex issues and was a useful addition to mannequin-based training.
Key perceived benefits included efficient training on rare events through unlimited repetition and ability to standardize experiences. This highlights VR’s capacity to provide immersive, consistent learning opportunities not easily replicated through traditional modalities.
Li, L. Gao, H. Yin et al. – Clinical Simulation in Nursing
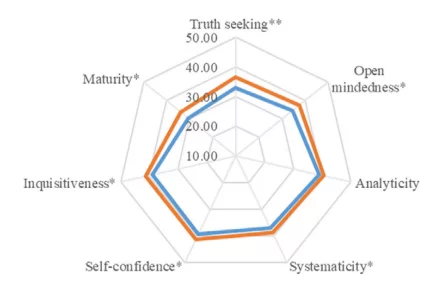
This study found that implementing a virtual reality-based cognitive assessment and rehabilitation simulation course significantly improved critical thinking skills in undergraduate nursing students. Specifically, scores increased across multiple domains including truth seeking, open mindedness, systematicity, self-confidence, inquisitiveness, and maturity.
Students also gave high satisfaction ratings for the virtual system, course, teaching, and self-evaluation. The results suggest this type of virtual reality simulation course provides an effective and novel teaching method to enhance critical thinking abilities in nursing education.
To find out more information about XR technology in simulation training, check out our evidence overview, trial the training software, or contact us for more information and any research questions!